Consult an Online Dentist to Get Dental Infection Treatment
What is a Dental Infection?
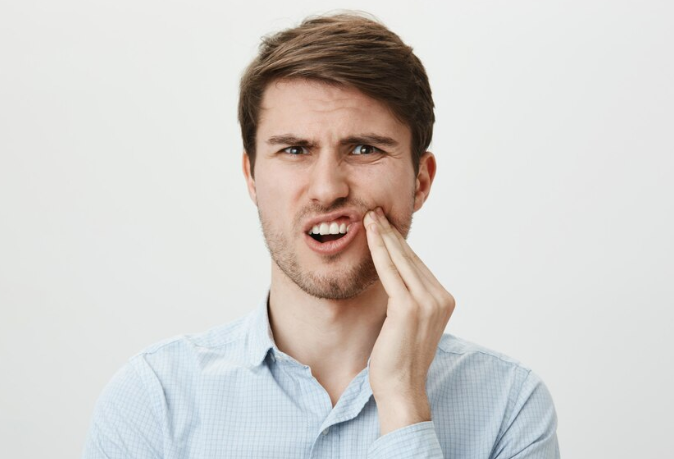
A dental infection, also known as a tooth abscess, can occur in different areas near the tooth. It occurs when bacteria invade the tooth and its surrounding tissues.
Various reasons cause dental infections, but bacteria are usually the root cause. A dental infection may be caused by periodontal disease, trauma to the tooth, or tooth decay. Common symptoms of this infection include tooth pain, sensitivity to hot or cold drinks and food, inflammation of the gums, and abscesses.
Abscesses can occur at the tip of the tooth's root (periapical) or in the gums at the side of a tooth root (periodontal). If you don't treat your dental infection, it can spread through other parts of the body to cause severe health complications.
If you have symptoms of a dental infection, fill out a virtual consultation form today to talk to our online dentist. Don't wait until your symptoms get worse!




 19 Oct 2024
19 Oct 2024